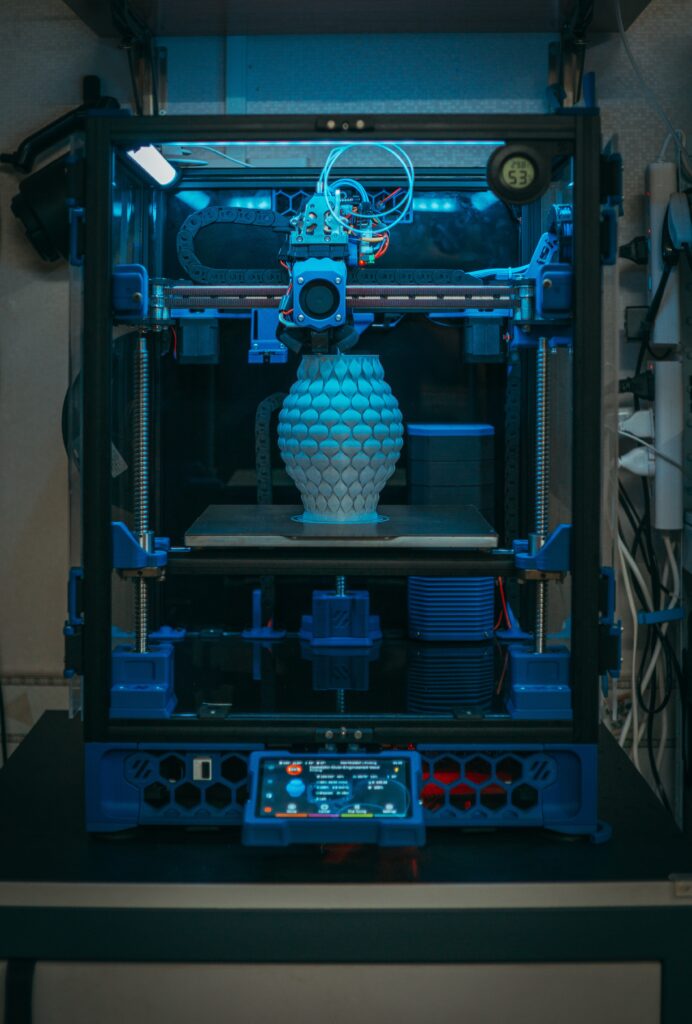
Additive manufacturing and subtractive manufacturing are two different methods used to create products, parts, and components.
Additive manufacturing, also known as 3D printing, is a process of building up layers of material to create a three-dimensional object. This is achieved by using a digital 3D model, which is sliced into thin layers, and then the printer deposits or solidifies the material layer by layer until the object is complete. This method is ideal for creating complex shapes and geometries, and is often used for rapid prototyping, customized parts, and small production runs.
Subtractive manufacturing, on the other hand, is a process of removing material from a block or piece of material to create a desired shape. This is typically done with tools such as mills, lathes, and routers, which cut away material from the starting block until the final shape is achieved. This method is more suitable for creating parts with simple geometries, and is often used for large production runs.
Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice between additive and subtractive manufacturing will depend on the specific requirements of the part or product being produced, as well as the production volume and time constraints. Additive manufacturing is generally more flexible and allows for more design freedom, while subtractive manufacturing is better suited for high-volume production runs and can produce parts with higher accuracy and precision.